Ever wondered how to keep your meals not just delicious but also safe? You’re in the right place! Food Safety Guidelines are your go-to for ensuring every bite is as safe as it is scrumptious. Dive in with us as we explore the simple steps to safeguard your kitchen from unwanted germs.
Food Safety Guidelines by Top 4 Institutions
Top institutions like the FDA and USDA set food safety guidelines to protect us. They say to always wash hands and surfaces, keep raw meats separated, cook to the “right “optimal” temperatures, and chill foods correctly. Following these steps reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses, keeping meals safe and enjoyable.
World Health Organization (WHO)

WHO wants to change how food is made and shared so that all meals stay safe to eat. They believe everyone should have access to food that helps them stay healthy and doesn’t harm our planet. WHO works with another group called the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) to make rules about food safety.
They have a big plan called the WHO Global Strategy for Food Safety that helps them do this from 2022 to 2030. They also have a team called INFOSAN that helps countries handle food emergencies, like when food might make people sick.
Note that WHO teaches people the Five Keys to Safer Food. These are easy tips that anyone can follow to keep food safe from germs that can make us sick.
- Keep It Clean: Washing your hands and keeping your kitchen clean are important first steps in ensuring that your food is safe to eat.
- Keep Them Apart: Always keep raw meats away from cooked dishes to avoid spreading germs.
- Cook Well: Make sure all your food is cooked all the way through. This kills any bad germs that might make you sick.
- Store at the Right Temperature: Keep your food in the fridge or freezer if it needs to be cold, and don’t leave it out too long.
- Choose Safe Ingredients: Use clean water and fresh ingredients when you make your meals.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has laid out four essential steps to ensure food safety: Clean, Separate, Cook, and Chill. Let’s start with “Clean.” The CDC emphasizes the importance of washing your hands and surfaces often to prevent the spread of germs that cause food poisoning.

Here’s how you can incorporate this step into your daily routine:
- Wash Hands Thoroughly: Before, during, and after food preparation, and before eating, wash your hands for at least 20 to 22 seconds with soap and water.
- Sanitize Surfaces: Regularly clean utensils, cutting boards, and countertops with hot, soapy water. Germs can reside on surfaces and utensils and contaminate the food you prepare.
- Rinse Produce: Under running water, rinse fresh fruits and vegetables to remove potential contaminants. Even if you plan to peel the produce, it’s important to wash it first to prevent the transfer of bacteria from the outside to the inside.
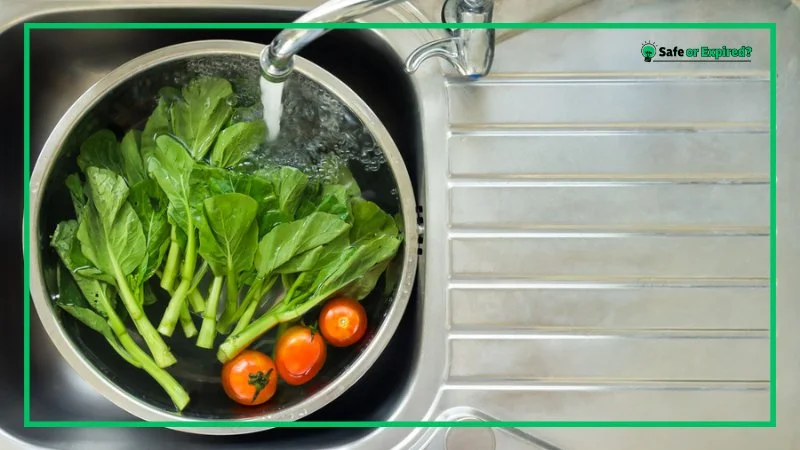

Now, the “Separate.” Remember that cross-contamination is a major cause of foodborne illnesses. Raw meat, poultry, seafood, and eggs, so keep them separated. Implement these practices to avoid cross-contamination:
- Use Separate Cutting Boards: Have one cutting board for all kinds of meat and another for fresh produce and ready-to-eat foods. This prevents germs from raw foods from contaminating foods that won’t be cooked.
- Store Foods Properly: In the refrigerator, store raw meat in sealed containers. If you can’t, wrap them securely to prevent juices from leaking onto other foods.
The Cook and Chill guidelines are simple. According to the CDC, cooking to the right temperature ensures harmful germs are killed. Moreover, a food thermometer is recommended for accuracy.
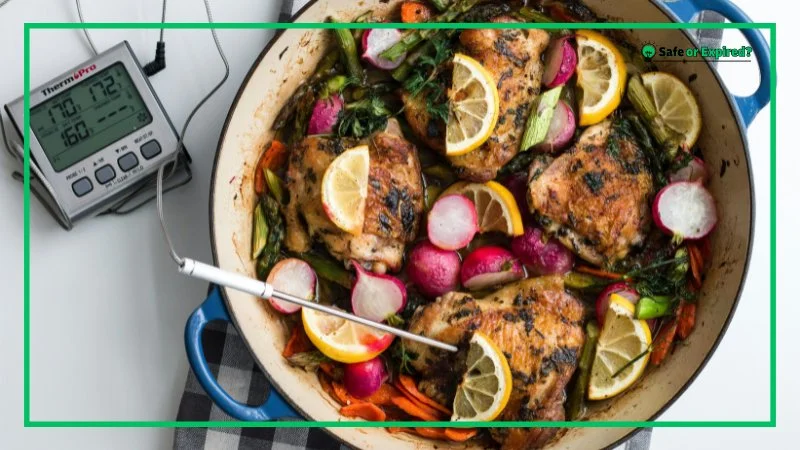

Here are the guidelines to remember:
| Food Type | Temperature | Additional Instructions |
| Whole cuts of beef, veal, lamb, and pork | 145°F | Rest for 3 minutes before carving/eating |
| Fish with fins | 145°F | None |
| Ground meats (beef, pork) | 160°F | None |
| All poultry (including ground chicken and turkey) | 165°F | None |
| Leftovers and casseroles | 165°F | None |
Lastly, the chilling. It requires refrigerating perishables promptly to inhibit bacteria growth, emphasizing the danger zone between 40°F and 140°F where bacteria multiply rapidly.
| Guideline | Details |
| Refrigerator Temperature | Keep at 40°F or below |
| Freezer Temperature | Keep at 0°F or below |
| Checking Temperature | Use an appliance thermometer if no built-in one |
| Storing Warm/Hot Food | Use shallow containers; refrigerate small portions quickly |
| Refrigerating Perishables | Within 2 hours; within 1 hour if above 90°F |
| Thawing Frozen Food | In the refrigerator, cold water, or microwave; not on counter |
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
FDA plays a crucial role in safeguarding Americans from foodborne illnesses, which affect an estimated 1 in 6 Americans annually. Despite the high safety standards, approximately 48 million cases of foodborne illness occur each year. That’s why you must follow FDA’s food safety guidelines.
Just like the CDC, the FDA emphasizes four cornerstone practices for food safety:
- Clean
- Separate
- Cook
- Chill.
These measures are particularly vital for individuals at higher risk of developing severe food-borne illnesses, such as pregnant women, young children, older adults, and those with weakened immune systems.
- Clean: Proper hand washing with warm water and soap for at least 20 to 22 seconds is recommended. Doing this before and after handling food, after using the bathroom, and after touching pets is essential. Surfaces, utensils, and produce should be washed thoroughly to eliminate potential contaminants.
- Separate: Prevent cross-contamination by keeping raw meats, poultry, seafood, and eggs away from other foods. This includes using separate cutting boards and ensuring cooked food does not come into contact with surfaces that hold raw meat without proper cleaning.
- Cook: Foods should be cooked to their safe minimum internal temperatures. This practice is the only reliable method to ensure harmful bacteria are killed, as color and texture are not accurate indicators of food safety.
- Chill: Prompt refrigeration of perishable items is necessary to prevent bacterial growth. The refrigerator should be set at 40° F or below. Wondering about the freezer? Well, the recommendation is 0° F or below. Leftovers should be cooled in shallow containers to speed up the chilling process, and food should never be thawed on the countertop.
FDA’s recommends these internal temperatures:
| Food Type | Temperature | Rest Time / Additional Info |
| Beef, Pork, Veal, Lamb | 145°F | 3-minute rest time |
| Ground Meats | 160°F | – |
| Poultry | 165°F | – |
| Eggs and Egg Dishes | – | Cook until yolk and white are firm; 160°F for dishes |
| Fin Fish | 145°F | None |
| Shellfish and Seafood | – | Cook until flesh is pearly and opaque |
U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA)

The USDA’s guidelines are pivotal for maintaining food quality (from farm to table) in the United States. They emphasize storage, thawing, preparation, cooking, and serving. In fact, these guidelines form a comprehensive blueprint for preventing foodborne illnesses.
Let’s start with storing food safely. The foundation of food safety begins with proper storage. So, follow these USDA guidelines about it:
| Storage Category | Guidelines |
| Refrigeration | Refrigerate perishables within 2 hours of purchase/preparation (1 hour if >90°F). |
| Freezer and Refrigerator Temperatures | Refrigerator at/below 40°F, Freezer at 0°F. |
| Meat Storage | Fresh poultry, fish, ground meats: use/freeze within 2 days. Other meats: use/freeze within 3-5 days. |
| Canned Goods | High-acid foods (e.g., tomatoes): store for 12-18 months. Low-acid foods (meats, vegetables): 2-5 years. |
If you’re interested in knowing about the shelf life of canned seafood, then you will surely love reading How Long Canned Tuna Lasts after expiration.
Now, the thawing. Thawing food safely is crucial to maintaining its quality and safety. So, follow these guidelines:
| Thawing Method | Guidelines |
| Refrigerator Thawing | Allows slow, controlled thawing. |
| Cold Water Thawing | Submerge in a leak-proof bag in cold water, change water every 30 minutes. Cook immediately after. |
| Microwave Thawing | Use for quick thawing. Cook immediately after to prevent bacterial growth. |
Let’s not forget Preparation Practices. Before the heat hits the pan, follow these USDA guidelines:
| Practice | Guidelines |
| Handwashing | Wash hands with soap and warm/lukewarm water. |
| Cross-Contamination | Have more than one cutting boards. You should also clean surfaces and utensils with hot, soapy water after cutting raw meats. |
Cooking food to the right temperature kills harmful bacteria. Therefore, always remember these USDA recommendations:
| Food Type | Guidelines |
| Meats | Steaks, chops, roasts: 145°F with a 3-minute rest. Ground meats: 160°F. |
| Poultry | Minimum of 165°F. |
| Eggs and Leftovers | Cook until the yolk and white are firm. Reheat leftovers to 165°F. |
If you’re wondering about serving and storing leftovers, then USDA has got you covered, too. Remember this:
| Aspect | Guidelines |
| Temperature Maintenance | Keep hot foods >140°F. Cold foods: <40°F. |
| Buffet Tips | Use warming trays and ice bowls to maintain temperatures. |
| Leftovers | Cool rapidly in shallow containers. Consume within 3-4 days or freeze. Reheat to 165°F. |
If thawed in the refrigerator, it’s safe to refreeze before or after cooking. If thawed by other methods, cook before refreezing. Remember: proper storage is critical to keep raw food fresh.

By adhering to the USDA’s food safety guidelines, you can ensure that your meals are not only delicious but also safe for everyone at the table. These practices, from storage to serving, play a vital role in protecting against foodborne illnesses.
Why Are Food Safety Guidelines Important?
Food safety guidelines are crucial as they prevent foodborne illnesses by controlling the growth of harmful bacteria. They ensure that food is stored, prepared, cooked, and served safely, reducing the risk of contamination and protecting public health. Adhering to these guidelines helps maintain food quality and promotes overall well-being.
Think of food safety like a superhero who protects us from getting sick. These rules help everyone who makes and serves food do it in a way that’s safe. This means chefs, farmers, and even our families at home know how to keep germs away from our food. When everyone follows these rules, it means we can eat our meals without worrying about feeling bad later.
Examples of Outbreaks Prevented by Following Food Safety Guidelines
Sometimes, when people don’t follow the food safety rules, they get sick. In fact, not following these guidelines can cause outbreaks. Here are the ones that we have avoided due to the instructions issued by top food authorities:
- E. coli in Ground Beef: Proper cooking to the recommended temperature of 162°F (71°C) has prevented numerous potential outbreaks of E. coli O157:H7, particularly in restaurants and fast-food chains.
- Listeria in Deli Meats and Soft Cheeses: Adherence to refrigeration standards and avoiding cross-contamination in food service establishments have prevented listeria outbreaks, especially important for pregnant women, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals.
- Norovirus in Restaurants and Cruise Ships: Implementing strict handwashing protocols and surface sanitization procedures has significantly reduced norovirus outbreaks in communal dining settings.
- Botulism from Home-Canned Foods: Educating the public about proper canning techniques and the importance of acidifying certain foods has prevented botulism, a potentially fatal illness.
- Hepatitis A in Produce: Following guidelines for washing and sanitizing produce, especially in food service, has helped prevent outbreaks of hepatitis A, which can be transmitted through contaminated fruits and vegetables.
Note that food safety is for everyone—kids, parents, and grandparents. These rules help make sure that every bite of food we eat is safe and won’t make us feel bad.
So, the next time you see someone cooking carefully or washing their hands before making a sandwich, they’re being food safety superheroes. And that’s very important because it helps us all stay happy, healthy, and ready to play or learn every day.
Conclusion
Embracing food safety guidelines is easier than you think and crucial for keeping your food enjoyable and worry-free. By keeping these key points in mind, you’re already on your way to a healthier kitchen:
- Cleanliness is Key: Always start and end with clean hands, surfaces, and utensils.
- Separation is a Savior: Keep raw and cooked foods apart to avoid cross-contamination.
- Cooking to Perfection: Use a thermometer to ensure food reaches safe internal temperatures.
- Chilling Matters: Store leftovers promptly to keep harmful bacteria at bay.
With these simple practices, you’re not just making meals; you’re ensuring each dish brings joy, not germs, to the table. Stay curious, stay cautious, and let’s make food safety a part of our daily recipe for success!